|
Chapter 1
Major Themes of Anatomy and Physiology |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Major Themes in Anatomy and Physiology |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide (4 Points). |
| |
|
* |
C1: Study Guide |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Video Homework Assignment (56 min of videos) |
| |
|
The Chapter Study Guide Questions and Video Worksheet Questions are required homework assignments. They are part of your grade. You will need to submit this work before we cover the topics in lecture. When you do the homework assignments, you are preparing for the unit exams. The test questions are taken from the study guide questions. |
| |
|
Video Homework Questions - Print PDF (Below are the links to the videos) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
Twenty Amazing Facts About the Human Body - 10 min |
| |
|
> |
Positive vs Negative Feedback ///
Negative Feedback's Role in Homeostasis - 15 min |
| |
|
> |
What is a reflex arc? - 2 min |
| |
|
> |
Natural Selection (and Evolution) - 7 min |
| |
|
> |
Fact vs Theory vs Hypothesis vs Law - 7 min |
| |
|
> |
How to Use the Feynman Technique - Study Tips - How to Study and Learn Anything - 5:45 min |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Special Bonus Point Quiz - (2 Points) -
You may receive two bonus points if you write this homeostasis definition before each unit exam.
|
|
| |
|
|
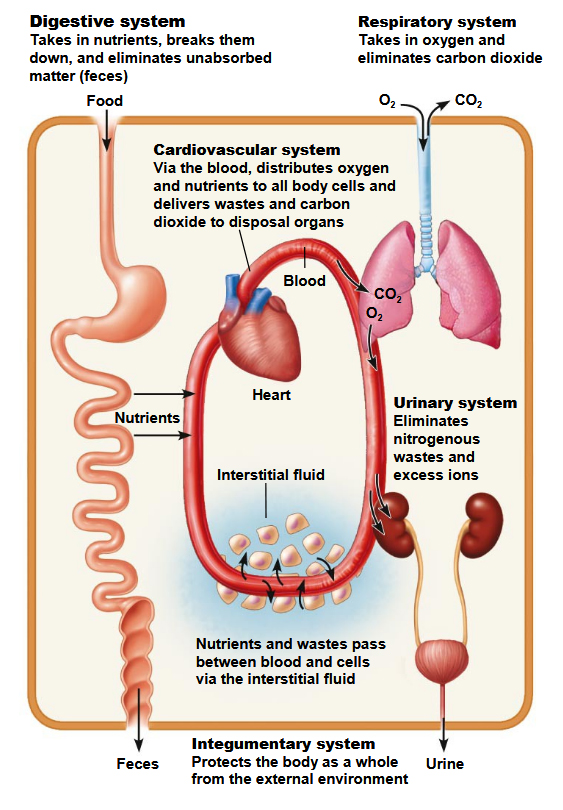
Homeostasis is the ability of a system to resist change. Human organs resist change in the internal environment. This is the interstitial fluid around our cells.
The interstitial fluid is in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Some organs bring nutrients into the interstitial fluid. Nutrients are transported into the cell's cytoplasm. Cells metabolize the nutrients for growth, repair, or to make new cells.
Cellular metabolism creates toxic waste. These molecules are secreted out of the cytoplasm and into the interstitial fluid. Organs excrete waste molecules out of our body. Negative and positive feedback mechanisms regulate the organs making homeostasis possible. Disease or death occurs when homeostasis fails. .
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
What Is The Best Way To Learn Anything? |
| |
|
** |
The best way to learn anything. by Dr. Richard Feynman PhD, theoretical physics and Noble Prize Winner (article) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Now is the time to learn the "Metric System" |
| |
|
** |
Metric System Basics (w answer key) //// Temperature Conversion Worksheet |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content below is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C1's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious students! |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Why do some students find science hard? Dr. Richard Feymen / Nobel Prize Winner - 60 min |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Evolution: This film explores what human hands, vision, and brains reveal about our evolution from ancient primate ancestors. Our primate progenitors had bodies a lot like those of modern monkeys and spent tens of millions of years living in trees. From them we inherited our versatile hands, amazing vision, and capable brains—but also some less beneficial traits, including our bad backs and terrible sense of smell. (60 min // HHMI) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
How Many Cells Are in the Human Body |
| |
|
* |
Introduction to Cell and Virus Structure - Size Matters |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Homeostasis (power-point lecture slides) |
| |
|
* |
Homeostasis |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
The Origins of Tetrapods // Tetrapods Evolved From Fish! |
| |
|
* |
Origins of Biomedical Science |
| |
|
* |
Evolution In Need of an Update |
| |
|
* |
Evolution, Natural Selection, and Adaptation |
| |
|
* |
The Timeline of Life (Taken From Wiki) |
| |
|
* |
Tarsier: Small Primate Unchanged in 45 Million Years |
| |
|
* |
Tarsier II |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
The History of Evolution from a Cell to Humans |
| |
|
* |
The Human Family Tree |
| |
|
* |
Understanding Evolution: This site was created by the University of California Museum of Paleontology with support provided by the National Science Foundation (grant no. 0096613) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (grant no. 51003439). |
|
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
The Ascent of Man (Video) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Dr. Richard Feynman, Phd was a theoretical physics. In this video, he talks about "taking the world from another point of view". Even before he completed his graduate studies, Dr. Feynman was asked to be part of the team at Los Alamos that developed the atomic bomb. He later won the Nobel Prize for his original work in physics. Feynman is celebrated as one of our most brilliant and original thinkers in theoretical physics. Dr. Feynman gave future generations of scientist a new way to think about the unknowable. // "Richard Feynman, the genius that he was, had the singular ability to realize that perspectives and points of view give us a window into all of the alternate possibilities that may exist. This is the definition of genius." (video 40 min) |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 2
Chemistry of Life |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
You need to know the structure and function of atoms, molecules, and macromolecules to learn human physiology. Your body is like a "test tube" of chemical reactions. Chemistry is essential knowledge.
If you lack basic knowledge about chemistry then you need to acquire this knowledge now before you start to study human physiology. You may do this by reading chapter two in the textbook, review my lecture slides, and watch a series of video tutorials about chemistry. Each video was selected to cover a chemistry learning objective. You may need to watch some of these videos several times before you understand the topic.
Chemistry questions are 20% of your unit one lecture exam so you need to know this information. Bring your questions to class! |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Periodic Table (Not Covered in Class / Not a Test Topic) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture). |
| |
|
* |
C2 - Learning Objectives |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Required Assignments (two hours of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF (On the Unit One Lecture Exam there will be one question from 20 of the 23 videos in this homework assignment! These are also topics that I will cover in my lectures.) |
| |
|
> |
How the Periodic Table Works (4:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Time-line of Atomic Models:
Dalton's to Thompson's to Rutherford's to Bohr's to Quantum (11 min) |
| |
|
> |
Ionic vs covalent bonds (4:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Ionic vs Covalent vs Polar Covalent Bonds (2:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Hydrogen Bonding -V2 (5 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is the difference between an acid, base, and a salt? (18 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is an isomer? (5:36 min) |
| |
|
> |
What are free radicals and antioxidants? (7 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic? (2 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is the difference between these mixtures: solution, colloid, and suspension? (5:48 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is a buffer? (6 min) |
| |
|
> |
What is the bicarbonate buffering system? (6:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Metabolism: catabolic vs anabolic. (1 min) |
| |
|
> |
Carbohydrates (4:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Lipids (11 min) |
| |
|
> |
Proteins (6 min) |
| |
|
> |
Nucleotides and nucleic acids (5:55 min) |
| |
|
> |
Biochemical Pathways (1:35 min) |
| |
|
> |
Oxidation-Reduction Reaction (13 min) |
| |
|
> |
Enzyme Action (1:45 min) |
| |
|
> |
Enzymes (1:14 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
|
* |
Chemical Basis of Life |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Understanding Organic Molecular Structures |
| |
|
* |
Know Your Molecules (Power-Point Slides) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C2's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
** |
Mendeleev's Periodic Table 1872 (8 min) |
| |
|
** |
Atom Structure Meets the Periodic Table (8 min) |
| |
|
** |
Atom Structure: Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons (13 min) |
| |
|
** |
Chemical Bonding Introduction: Hydrogen Molecule, Covalent Bond & Noble Gases (7 min) |
| |
|
** |
Oxygen, Nitrogen, & Carbon and Covalent Chemical Bonds (18 min) |
| |
|
** |
Borh's Model of the Atom (video explains spectrum lines of hydrogen) |
| |
|
** |
Interactive Periodic Table of Elements (Los Alamos National Laboratory) |
| |
|
** |
Osmosis |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
** |
Biochemistry: Professor Dave's 28 videos covering biochemistry. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
** |
Richard Feynman Explains the Big Misconception About Electricity |
| |
|
* |
Why Light Speed Is The Limit? What Feynman Uncovered Will Collapse Your Mind |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Brownian Motion: Pollen in Water (Two of Einstein's 1905 Five Miricle Year Papers) |
| |
|
* |
How Much of an Atom Is Empty Space ? |
| |
|
* |
Understanding Atom and Their Electrons? (More advanced then what we need to know) |
| |
|
* |
Nanotechnology: The High Tech Revolution - with Dave Blank (Very Special!) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Where did the Universe come from? Geraint Lewis / RI Lecture |
| |
|
* |
The Origin of Elements |
| |
|
* |
The Periodic Table (Wiki) |
| |
|
* |
Mendeleev: The Father of the Periodic Table |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Michael Faraday - In the 1800's Faraday was the greatest experimental physicist. Faraday discovered electromagnetic fields,electromagnetic induction, refrigeration, benzene, and other important discoveries. Farada's work led to the electric motor and air conditioning which we use today! Furthermore, Faraday was the first scientist to think and recognize "fields". This idea is currently on the cutting edge of theoretical physic study today. It is said that Albert Einstein had only two photographs in this study, one was Michael Faraday. |
| |
|
* |
How did Michael Faraday invent? Royal Institue with David Ricketts |
| |
|
* |
Michael Faraday: The Art of Genius |
| |
|
* |
Demonstration of a Faraday Motor |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
What are the four forces of the universe? - These forces formed as a result of the "big bang". These same forces also resulted in atoms, chemistry and life itself. (Illustration Only ////// Video -> The Four Natural Forces: Gravity, Weak Nuclear Force, Electromagnetic, and Strong Nuclear Force. (Kahn Academy). |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
What Does An Atom Really Look Like? |
| |
|
* |
What is a Cathode Ray Tube? |
| |
|
* |
J.J. Thompson's Cathode Ray Tube Experiment (The Discovery of the Electron) /// Thompson's Model of the Atom |
| |
|
* |
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment - Rutherord's Atomic Model |
| |
|
* |
Milliken's Oil Drop Experiment (How the Charge of an Electron Was Determined) |
| |
|
* |
An Explaination of Neutrinos |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
The Physics of Life: How Water Folds Proteins / by Dr. Sylvia McLain (Royal Institute) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
** |
All About Chemistry: Annenberg Learner's mission is to "Advance Excellent Teaching in American Schools." Join with experts to observe chemistry in action and learn the laws and principles of this dynamic field. Computer technology and special effects place students in a front-row seat to observe many processes, even those that are too dangerous or impractical to experience directly. There are 26 videos in this series. |
|
|
| |
|
* |
Physics for the 21st Century: Explore the frontiers of physics research with the scientists on the front lines in this 11-unit course in modern phsics for high school physics teachers, undergraduate students, and science enthusiasts. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
The Character of Physical Law - The Law of Gravitation by Dr. Richard Feynman PhD |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Beta decay and positron decay explains how an atom with too many neutrons or too many protons may change their nucleus to become a more stable atom. So it is possible for carbon(C6) to "transmute" into boron (B5) or nitrogen (N7). This was the dream of the alchemist, however. It is not possible to turn carbon into gold! |
| |
|
* |
Beta Decay |
| |
|
* |
Positron Decay |
| |
|
* |
Alpha Decay |
| |
|
* |
What are alpha, beta, and gamma decay? (14 min video) |
| |
|
* |
Electron Capture (Occurs when ath atom has to many protons) |
| |
|
* |
Free Radicals (detailed explanation - how formed and damaged caused) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
E = MC2 |
| |
|
* |
A Brief History of Quantum Mechanics // Sean Carroll |
| |
|
* |
An Introduction to Quantum Biology by Philip Ball (Royal Institute // (One of the Best Lectures on Topic)) |
| |
|
* |
An Introduction to the Standard Model (graphic with text) |
| |
|
* |
Paul Dirac: The Most Beautiful Equation (discovery of anti-matter) |
| |
|
* |
The Standard Model: The standard model is the name given in the 1970s to a theory of fundamental particles and how they interact. It incorporated all that was known about subatomic particles at the time and predicted the existence of additional particles as well. When this video was made, a yet found but predicted sub-atomic particle called the Higgs was still not discovered. The Higgs particle was discovered 50 years after it was predicted in 2012!. |
|
|
| |
|
* |
The Standard Model (Fermilab scientist Don Lincoln describes the Standard Model of particle physics) |
| |
|
* |
How the Higg's Particle Completed the Standard Model by Harry Cliff at Ri, |
| |
|
* |
CERN: Standard Model of Particle Physics. |
| |
|
* |
Quantum Fields: Fields Are the Real Building Blocks of the Universe - with David Tong (60 min.) |
| |
|
* |
Standard Model Outlined |
| |
|
* |
TED Talk: Quantum Physics For Seven Year Olds by Dominic Walliman. /// or How to Teach and Learn Science! |
| |
|
* |
String Theory Explained |
| |
|
* |
Quantum Biology and the Hidden Nature of Nature (1:35) |
| |
|
|
Quantum Biology: An Introduction to the Far Edge of Biology!. |
| |
|
* |
Everything and Nothing: What is nothing? by Jim Al Khalili |
| |
|
* |
What is fire? (Explained using chemistry and physics) |
| |
|
* |
How to Make Soap |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
** |
The Year of Albert Einstein --- In 1905, Einstein was 26 years old. He received his PhD in physics but could not find a job as a professor. He was frustrated and needed work. So Einstein accepted a position as a patent clerk and in his spare time between March and June, he wrote five scientific papers that changed the world forever! One of these papers help to launch a new branch of science called quatum mechanics that made things like modern computers, cell phones, and GPS possible. He changed our understanding of the universe and how we live today |
| |
|
* |
Albert Einstein's special relativity /// image 2 /// image 3 /// image 4 /// image 5 /// time dialation /// length contraction |
| |
|
* |
Albert Einstein's general relativity /// Spacetime image 1 /// Spacetime image 2 /// Spacetime image 3 /// Spacetime image 4 |
| |
|
* |
Simple Idea Behind Einstein's Greatest Discovery |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Free Radical Formation (hterolysis vs homolysis of covalent bond) |
| |
|
* |
Octet Rule |
| |
|
* |
Alpha Particles |
| |
|
* |
Beta Particles |
| |
|
* |
Gamma Particles |
| |
|
* |
Electron Capture |
| |
|
* |
Positrons |
| |
|
* |
Electromagnetic Effect |
| |
|
* |
Photoelectric Effect |
| |
|
* |
Nuclear Fission |
| |
|
* |
Quantum Mechanic Model of the Atom (How it differs from Bohr's Model) |
| |
|
* |
Quantum Numbers, Atomic Orbitals, and Electron Configuration |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Origins of the Universe 101 / National Geographic (5 min) |
| |
|
* |
Mystery of Matter - Out of Thin Air / One of science’s great odd couples—British minister Joseph Priestley and French tax administrator Antoine Lavoisier—together discover a fantastic new gas called oxygen, overturning the reigning theory of chemistry and triggering a worldwide search for new elements. Soon caught up in the hunt is science’s // video / 54 min |
|
|
| |
|
* |
Mystery of Matter - Unruly Elements /Over a single weekend in 1869, a young Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev invents the Periodic Table, bringing order to the growing gaggle of elements. But this sense of order is shattered when a Polish graduate student named Marie Sklodowska Curie discovers radioactivity. //video / 53 min |
|
|
| |
|
* |
Mystery of Matter - Into the Atom/ Caught up in the race to discover the atom’s internal parts—and learn how they fit together—is a young British physicist named Harry Moseley, who uses newly discovered X-rays to put the Periodic Table in a whole new light. And a young American chemist named Glenn Seaborg creates a new element . // video / 55 min |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 3
Cellular Form and Function |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class. |
| |
|
* |
Cell Structure and Function |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture) |
| |
|
* |
Cell Structure and Function |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (75 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
The Wacky History of the Cell Theory - 6 min |
| |
|
> |
Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion & Active Transport: Movement Across the Cell Membrane (5 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
A Tour of a Cell (14 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
How Mitochondria Make ATP (1:42 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
* |
Anatomy of a Cell |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C3's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
* |
Cell Animation / Harvard University Animation (Full Version - 8 min / narrated) |
| |
|
* |
WBC Phagocytosis of Bacteria |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Kreb Cycle (Royal Institue Lecture) - What is the origin of life? Find out here! |
| |
|
* |
Finding Cancer: Biomarkers |
| |
|
* |
Trans Membrane Proteins - Khan Academy |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Mitochondria // Ninja Nerd (60 min) |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Cell Animation / Harvard University Animation ( Short Version - 3 min / not narrated) |
| |
|
* |
Motor Proteins (HHMI) |
| |
|
* |
Electron Transport Chain (Indtro) - BioVisions Video - Harvard University |
| |
|
* |
Electron Transport Chain (More Details) // BioVisions Video - Harvard University |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Origin of Cellular Life on Earth // Dr. Jack Szostak (Harvard / HHMI) Part 1 |
| |
|
* |
Protocell Membranes // Dr. Jack Szostak (Harvard / HHMI) Part 2 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Quantum Biology: How Physics Can Revolutionise Biology |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
The Nano-particles in Biology and Synthetic Biology with Sonia Contera (RI Video) |
| |
|
* |
Brownian Motion: The Force Able That Moves Nano-Strings |
| |
|
* |
Tensegrity: Forces That Form and Shape the Cytoskeleton - Buckminister Fuller |
| |
|
* |
The Clock Within Our Cells - Illustration Part A // Illustration Part B // Reference Artcle |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Chapter 4
Genetics and Protein Synthesis |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Cell Division - Cell Cycle - DNA Replication - Mitosis - Meiosis |
| |
|
* |
Protein Synthesis |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Genetics, Cell Division and Protein Synthesis |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (70 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
The Cell Cycle (3:43 min)
|
| |
|
> |
How Mitosis Works (6 min) |
| |
|
> |
Meiosis (7 min) |
| |
|
> |
Telomere and telomerase (2 min video animation) |
| |
|
> |
Modern Genetics (6:25 mn) |
| |
|
> |
DNA Replication 1 (1:26 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
Protein Synthesis Animated (19 min) |
| |
|
> |
CRISPR-Cas9 (7 min) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Not required but a deeper understanding of homework topics!!! |
| |
|
* |
So What is CRISPR Cas9? / More about but not part of homework assigment |
| |
|
* |
Meiosis by Professor Dave (10 min) - A more detailed explaination |
| |
|
* |
Mendelian Genetics and the Punnet Square by Professor Dave |
| |
|
* |
Chromosomes Structure and Function by Professor Dave |
| |
|
* |
Meiosis Phases by Bozeman Science.. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C4's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
** |
What Separates Humans from Chips? by Aeife McLysaght |
| |
|
** |
Genetic Mutations and Disease (Poster) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Copy Number Variation and the Secret of Life // Aoife McLysaght (Royal Institute) |
| |
|
* |
"Out of the Lab, and Into Society" talk by Aeife McLysaght at the Electric Picnic 2014 |
| |
|
* |
Where Do Ideas Come From -- Dr. Aoife McLysaght PhD // Ted Talk - 15 min. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Telomere and telomerase (6 min video w more detailed presentation) |
| |
|
* |
Telomere Length in Birds Predicts Longevity |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Introduction to Genes by Professor Aoide McLysaght |
| |
|
* |
Gene Expression - Initiation of Transcription (1:46 min) |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Genetic Mutations and Diseases |
| |
|
* |
Cell Cycle (Advanced Review) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Epigenetics Illustration SA |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Living Circuits - Using Microbes to Cure Diseases in Humans |
| |
|
* |
RNA in the Proto-Life Soup |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
How to Build a Dinosaur (15 min) |
| |
|
* |
Chimps, Bonobo, and Humans Are Linked by 98.7% of Our Common Genes |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
DNA's "Digital" Storage Capacity (2) |
| |
|
* |
Down Syndrome / Trisomy 21 |
| |
|
* |
Twist of Fate / How Cytoskeleton and Matrix Interact to Regulates Cell Division |
| |
|
* |
Living Curcuits Inside Bacteria May Cure Diseases in Humans |
| |
|
* |
Living Curcuits: Making Cellular Applications with DNA |
| |
|
|
| |
|
* |
CRISPR: (Video) New Knowledge Advances Biology / Geneticist Jennifer Doudna co-invented a groundbreaking new technology for editing genes, called CRISPR-Cas9. The tool allows scientists to make precise edits to DNA strands, which could lead to treatments for genetic diseases … but could also be used to create so-called "designer babies." Doudna reviews how CRISPR-Cas9 works — and asks the scientific community to pause and discuss the ethics of this new tool. |
|
|
| |
|
* |
CRISPR-Cas9: Recent Update on Technology |
| |
|
* |
CRISPR-cas9: (Video) Example of an advancement in basic science leading to new therapies in medicine. This technology will lead directly to cures for many genetic diseases. |
|
|
| |
|
* |
CRISPR: (Video) Genome Editing with CRISPR-Cas9: McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT |
|
|
| |
|
* |
CRISPR-cas9: (Article) The Gene Genie |
| |
|
* |
CRISPR-cas9: (Article) Wiki Review |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Molecular Genetics I/ Dr. Robert Sapolsky |
| |
|
* |
Molecular Genetics II / Dr. Robert Sapolsky |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 5
Histology |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Tissue Growth and Change |
| |
|
* |
Tissue Repair and Wound Healing |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture). |
| |
|
* |
C5: Learning Outcomes |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review |
| |
|
* |
Tissues |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (21 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
Introduction to Histology - V1 (14 min) |
| |
|
> |
Introduction to Histology - Omit this video |
| |
|
> |
Intracellular Junctions (6:41 min) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C5's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
* |
Introduction to Histology (37 min) - comprehesive with many slide examples |
| |
|
* |
Images - Slide Show: Various Tissues MRI False Color |
| |
|
* |
First Hints That Stem Cell Therapy Can Help Patients Get Better |
| |
|
* |
Burns |
| |
|
* |
Skin Cancer |
| |
|
* |
Skin Color |
| |
|
* |
Hair and Nails |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 6
The Integument System |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class. |
| |
|
* |
The Integument System (Skin) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Burns (Not Covered in Class / Not a Test Topic) |
| |
|
* |
Skin Cancer (Not Covered in Class / Not a Test Topic) |
| |
|
* |
Skin Color (Not Covered in Class / Not a Test Topic) |
| |
|
* |
Hair & Nails (Not Covered in Class / Not a Test Topic) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture) |
| |
|
* |
C6 - Learning Outcomes |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
|
* |
Skin and Its Appendages |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (35 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
Introduction to the Integumentary System ( 14 min) |
| |
|
> |
National Geographic: Skin (5:30 min)) |
| |
|
> |
Burns: First, Second, and Third (8:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
Skin Cancers (5:24 min) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C6's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
** |
How We Get Skin Color (3 min video // HHMI) |
| |
|
* |
Sick People Smell Bad |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Burns |
| |
|
* |
Skin Cancers |
| |
|
* |
Nails and Hair |
| |
|
* |
Skin Color |
| |
|
* |
Pathophysiology: Skin Disorders |
| |
|
* |
Images Only / Integument |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
|
Chapter 7
Bone Tissue |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Bone Tissue // Bone Development // Bone Fracture and Repair // Osteoporosis |
| |
|
* |
Introduction to the Skeletal System (Lab Content - Review In Lecture) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture) |
| |
|
* |
C7: Learning Outcomes |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review |
| |
|
* |
Skeletal Tissue |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (30 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
Bone Structure and Type (7 min) |
| |
|
> |
Interstitial and Appositional Bone Growth (3 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
Bone Remodeling and Repair (6:30 min) |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C7's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Haemophilia: Joint Effort |
| |
|
* |
Pathophysiology: Musculoskeletal Disorders |
| |
|
* |
Bone Tissue / Only Images |
| |
|
* |
Titanosaur Fossils: Image 1 - Image 2 - Image 3 |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 8
The Skeletal System
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
|
The structure of the skeletal system is covered in lab.
Your textbook covers the skeletal sysem in C7 and C8. Some of these PowePoint presentations are posted for reference material. However, some of the information in in the first PwPt, Introduction to the Skeletal System has content that will also be covered on the lecture exam and required as part of our Lecture Objectives (see Study Guide below). |
|
|
| |
|
* |
Introduction to the Skeletal System |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
|
* |
Skeletal System |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C8's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
** |
Chimpanzee and Human Anatomy and the Evolution of Language |
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
|
| |
|
* |
Is this a smart way for women to walk? |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
* |
Axial Skeleton / Only Images |
| |
|
* |
Appendicular Skeleton / Only Images |
| |
|
* |
Pectoral Girdle |
| |
|
* |
Pelvic Girdle |
| |
|
* |
Images Only of Appendicular Skeleton System |
| |
|
* |
Scapula Provides New Insight About Homanid Evolution |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
| |
Chapter 9
Joints |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Introduction and Classification of Joints |
| |
|
|
Note: Preview lecture slides // no C9 Study Guide or Video Homework. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review / Highly Recommended |
| |
|
* |
Articulations |
| |
|
* |
Skeletal Joints |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C9'slearning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
More About Joints |
| |
|
* |
See Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 10
The Muscle System |
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Correlate to Learning Objectives |
| |
|
* |
Introduction to the Muscle System |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C10's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
* |
Skeletal Muscle Images |
| |
|
* |
Botulinum Toxin (Botox) |
| |
|
* |
More Articles of Interest / Archival |
| |
|
* |
Pathophysiology: Musculoskeletal Disorders |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Important Notice for C8-C9-C10
The Science Department has removed C8 and C10 as comprehesive lecture topics.
However, some essential information from C8, C9, and C10 will be discussed in class.
A special
powerpoint presentation and an amended Study Guide for these three
chapters is
posted below.
Power Point Covering Essential Info for C8, C9, and C10
Study Guide for the Essential Info for C8, C9, and C10 |
| |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 11
Muscle Tissue
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Lecture Slides / Preview Slides Before Class |
| |
|
* |
Muscular Tissue. |
| |
|
* |
Nerve Muscle Relationship, Contraction Cycle, and Motor Units |
| |
|
* |
Length Tension Relationships / Muscle Behavior / Fiber Classes |
| |
|
* |
Muscle Energy / Metabolism / Fatigue. |
| |
|
* |
Smooth Muscle and Cardiac Muscle. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Study Guide /Complete Before Class (Bring Your Questions to Lecture) |
| |
|
* |
C11: Learning Outcomes |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Chapter Audio Review |
| |
|
* |
Physiology of the Muscle System |
| |
|
* |
Anatomy of the Muscle System |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Homework Assignments (25 min of videos) |
| |
|
Homework Video Questions - Print PDF |
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
|
| |
|
> |
Myosin Heads Interacting with Actin (skip this video) |
| |
|
> |
Myosin Heads and Actin Filament (2:25 min) |
| |
|
> |
Sliding Filament Theory V3 (7 min) |
| |
|
> |
Stretch Reflex (9 min) |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
The following content is NOT REQUIRED, however. It does correlate to C11's learning objectives. The information is included only for the curious! |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
* |
Stretch Reflex (detailed explanation) (34 min) |
| |
|
* |
Length Tension Relationship in Skeletal Muscles... |
| |
|
** |
Muscles -- Anatomy Revealed Slide Presentation |
| |
|
* |
Sliding Filament Theory / Test Your Knowledge About the Skeletal Muscle's Structure & Function |
| |
|
* |
Electrophysiology: Demonstrating Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Function (Plus Control Transfer) |
| |
|
* |
Atomic Force Microscope - Myosin Motor Movement |
| |
|
* |
Evolved to Exercise (SA) - Unlike our ape cousins, humans require high levels of physical activity to be healthy. |
| |
|
* |
What Does Running Do To the Brain? |
| |
|
* |
Muscle Pathology |
| |
|
* |
See Articles of Interest / Archival |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|